Capture
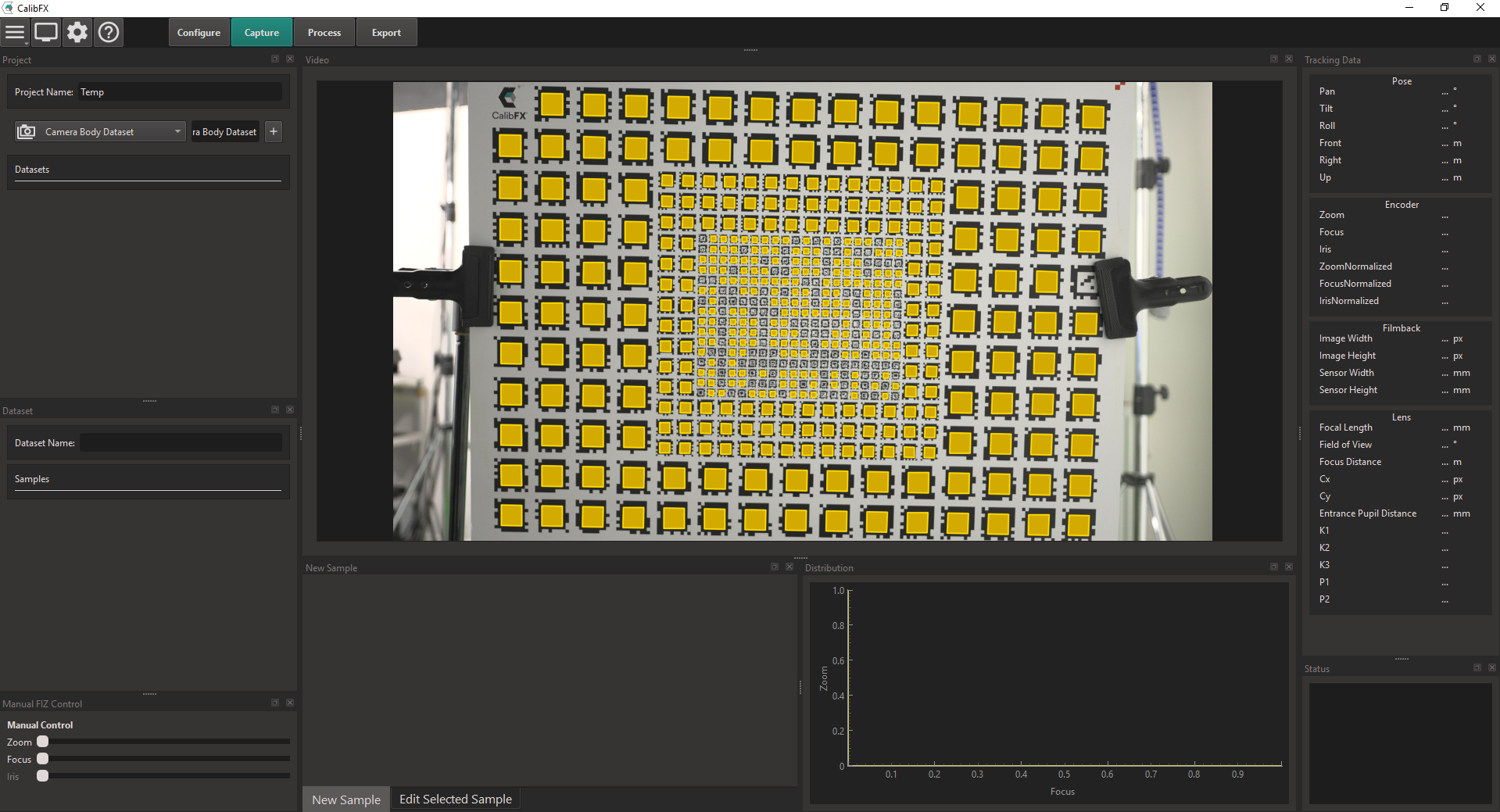
1. Project
You can start by naming the calibration project in the "Project Name" text field.
Then you will have to add several datasets to this project.
The following dataset types will always be required for the calibration process :
- a Camera Body Dataset
- a Focus Distance Dataset
- a Focal Length Dataset
- several Picture Datasets
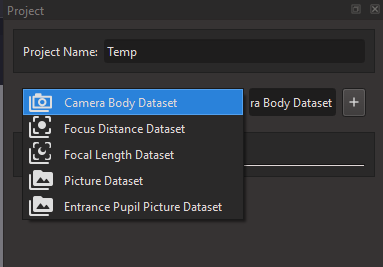
To add a dataset, select the desired type and press the "+" button.
You can pre-create the datasets before filling them up. The recommended minimum datasets are the following:
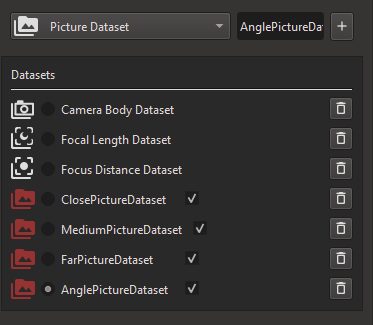
Note
You should have at least 4 Picture Datasets, including one with inclination of the board.
2. Dataset
2.1. Camera Body Dataset
The Camera Body Dataset specifies the effective sensor size and resolution.
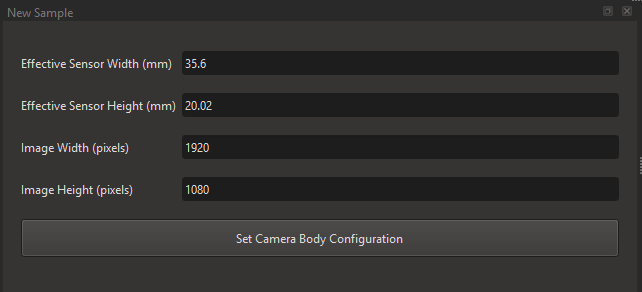
You only need to create one sample for the camera body dataset.
Warning
Some cameras crop the footage between resolutions. In this case, there will be issues with the sensor size as the effective sensor size is not the size given by the manufacturer. It is sometimes possible to calculate the effective sensor size with a cross-multiplication on the resolutions.
2.2. Focal Length Dataset
The Focal Length Dataset stores the focal length indications on the lens barrel.
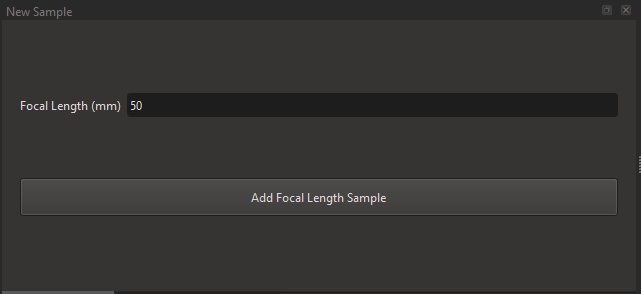
You only need the minimum and maximum indicated focal lengths.
On the lens, move the zoom control to minimum, write down the written value and press "Add Focal Length Sample", then move it to maximum, write the max value and press the button again.
Warning
The values needed here are in milimeters.
2.3. Focus Distance Dataset
The Focus Distance Dataset stores the focus distance indications on the lens barrel, or measurements done by the user.
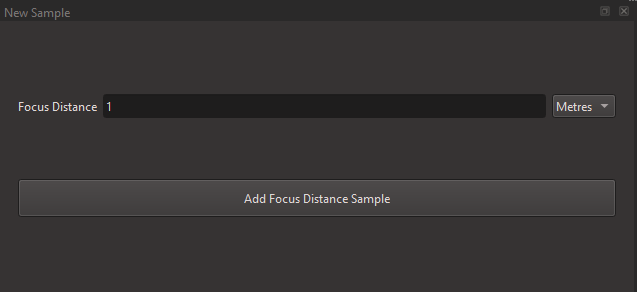
On the lens, successively move the focus control to each written value, report it in the software, and press "Add Focus Distance Sample".
Warning
The values needed here are either in meters or feet.
Note
If you don't have access to the markings on the lens, or don't trust the manufacturer, you can place an object at different distances, focus on it and measure the distance to the camera sensor (indicated by a little Phi symbol).
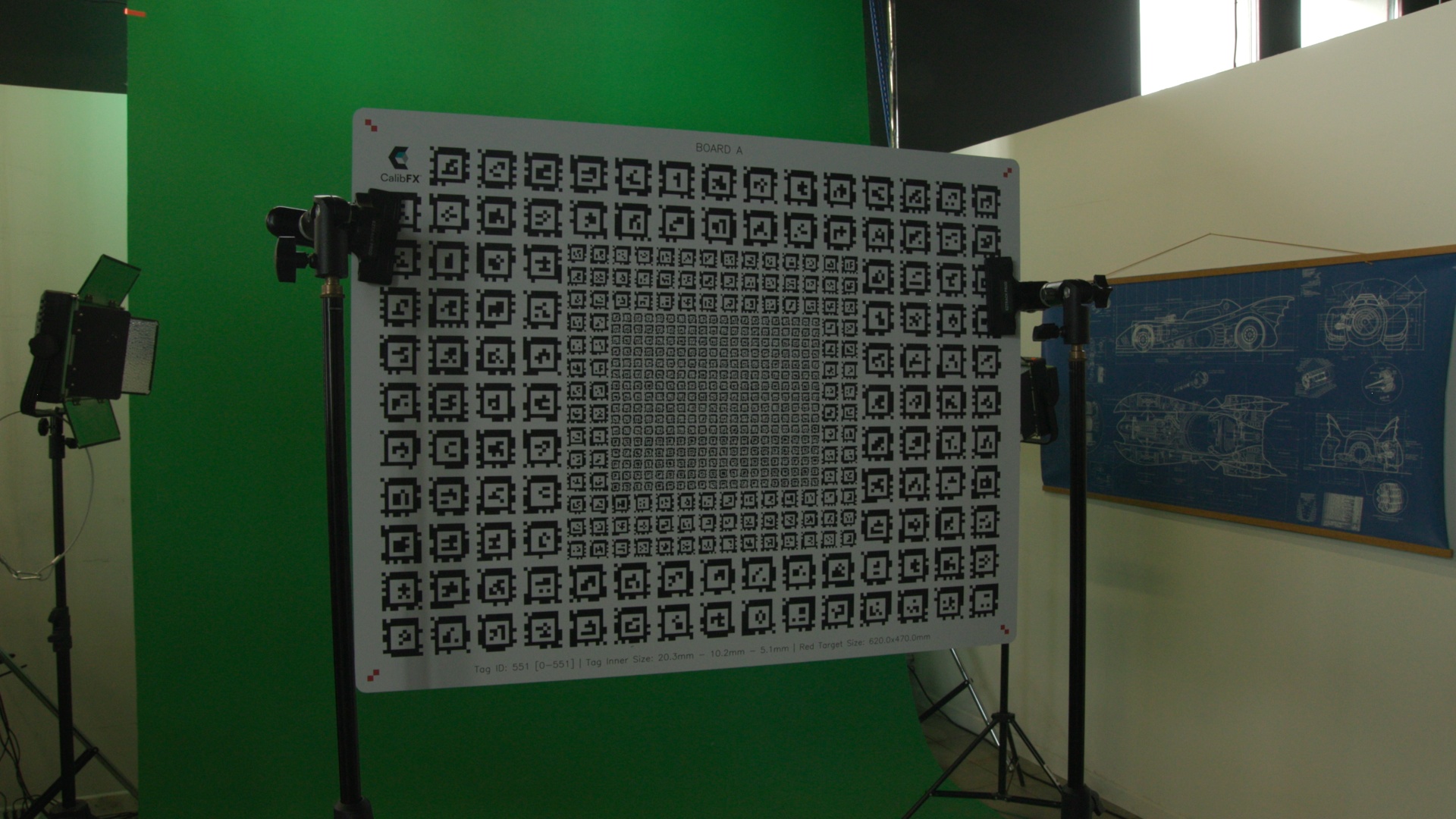
2.4. Picture Dataset
A Picture Dataset stores images along with tracking data.

For the solving to work, the camera and board must stay absolutely static for the entire duration of a Picture Dataset. Once you move either in space, you should not add any more pictures to this picture dataset. Create a new one instead, indicating a new Camera-Board position.
Tip
You want to maximize depth of field when taking pictures, so turn on some lights and close the iris as much as possible on the lens.
3. Recommended Pictures
The 4 recommanded datasets have the following board position and recomanded board :
- close (A)
- medium (B if your lens has a shallow zoom, A otherwise)
- far (B)
- angle (A)
From the camera's point of view, it would look something like this in wide angle:

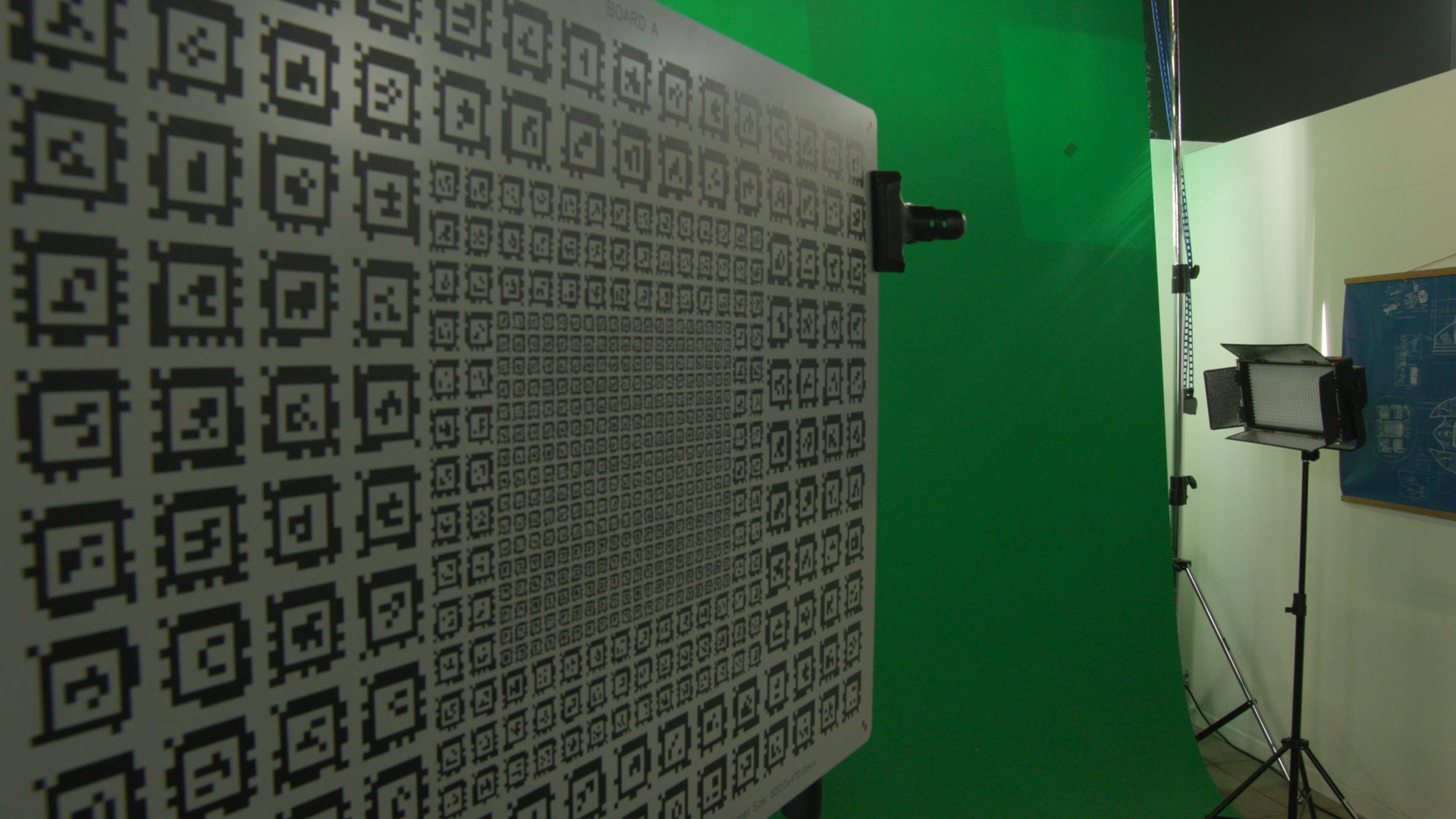
For each picture dataset, you should then cover the Zoom and Focus space with samples:
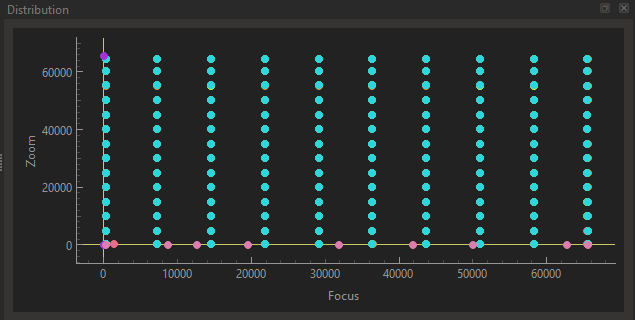
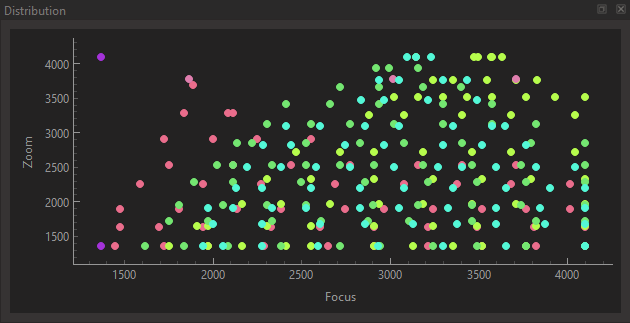
Both of these examples are very good.
- The first one was made automatically and took many out of focus pictures. This is not problematic as the data is very dense so there is still enough for solving.
- The second one was made manually, by moving zoom and focus remotes. The operator moved the zoom by increments of 0.1 and within a zoom level moved the focus from the close and far limit of the DoF, hence the conical shapes.
Warning
You should not touch the lens while taking pictures as it causes micro-movements that can induce errors in the solver, since it assumes board and camera are static within a dataset!
You can proceed to the next step of the calibration by clicking on the "Process" Button at the top.